Why Hemp Protein's Amino Acid Profile Changes Everything

This screenshot highlights the nine essential amino acids. These are the fundamental building blocks our bodies can't produce on their own, making dietary intake absolutely crucial. Why does this matter so much? Because hemp protein uniquely provides all nine, a true rarity in the plant-based protein world.
Imagine building with LEGOs. You need all the right bricks (amino acids) to create a complete structure (protein). Many plant proteins are missing a few key pieces, making it tougher for your body to build and repair tissues. Hemp protein, however, comes with the full LEGO set!
This complete amino acid profile isn’t just a nutritional checkbox; it fundamentally changes how your body utilizes this protein.
Hemp Protein: A Complete Protein Source
The amino acid profile of hemp protein boasts all nine essential amino acids our bodies require, making it a complete plant-based protein source—a real standout.
To give you a closer look, let's break down the composition: histidine (1–2%), isoleucine (2–3%), leucine (nearly 5%), lysine (2–3%), methionine (slightly over 1%), phenylalanine (around 3%), threonine (2–3%), tryptophan (approximately 1%), and valine (around 3%). This balanced composition empowers your body to efficiently use the protein for vital functions like muscle building and tissue repair. For an even deeper dive, check out this resource: Hemp Protein: Valuable Nutrients & Amino Acids with Good Tolerance.
This significant advantage sets hemp protein apart from other plant-based options, such as pea or rice protein, which often lack one or more of these essential amino acids. This is a game-changer for those following a vegan or vegetarian lifestyle, or anyone simply seeking to diversify their protein intake. Interested in learning more? The Amino Acid Profile of Hemp Protein: Why It’s Better Than Other Plant Proteins offers a great comparison.
The Impact of a Complete Amino Acid Profile
Having a complete amino acid profile doesn't just mean ticking a nutritional box. It profoundly affects how effectively your body uses the protein, impacting everything from muscle recovery after a workout to overall health and well-being.
To better illustrate the composition of hemp protein, let’s take a look at the following table:
Hemp Protein Essential Amino Acid Breakdown
Complete breakdown of all nine essential amino acids found in hemp protein with their typical percentages
| Essential Amino Acid | Percentage of Total Amino Acids | Primary Function in Body |
|---|---|---|
| Histidine | 1-2% | Growth and repair of tissues; production of red and white blood cells |
| Isoleucine | 2-3% | Muscle metabolism; wound healing; immune function |
| Leucine | ~5% | Muscle protein synthesis; regulation of blood sugar levels |
| Lysine | 2-3% | Calcium absorption; collagen formation; hormone and enzyme production |
| Methionine | ~1% | Metabolism; detoxification; tissue growth |
| Phenylalanine | ~3% | Production of neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine |
| Threonine | 2-3% | Collagen and elastin formation; immune function; fat metabolism |
| Tryptophan | ~1% | Production of serotonin and melatonin; supports mood and sleep |
| Valine | ~3% | Muscle growth and repair; energy production |
As you can see, hemp protein provides a valuable source of all the essential amino acids, each playing a crucial role in various bodily functions. This makes hemp protein a potent ally in supporting your overall health and wellness.
The Essential Nine: What Your Body Desperately Needs Daily
Think of your body as a bustling construction site. Bricks, wood, wiring – these are the basic materials needed to build a house. Your body also has essential building blocks, and those are amino acids, the foundation of protein. Nine of these amino acids are essential, meaning your body can't produce them on its own – you have to get them through your diet.
Each essential amino acid plays a unique and vital role, like specialized workers on that construction site. Leucine, for example, is like the repair crew, helping your muscles recover after a tough workout. Tryptophan, on the other hand, is more like the site manager, influencing your mood and sleep.
This image shows the basic structure of an amino acid – a sort of blueprint for these tiny building blocks. Notice the carboxyl group, the amino group, and the side chain (labeled "R"). This side chain is what makes each amino acid unique, determining its specific job within the body. These amino acids link together to form proteins, the complex machinery that keeps everything running smoothly.
Now, back to our construction site analogy. Imagine trying to build a house without enough nails. Even something seemingly small can hold up the entire project. Similarly, if you're missing even one essential amino acid, your body's "construction" projects – building and repairing tissues, producing hormones, and more – can be compromised. That's where hemp protein comes in.
Why Complete Proteins Matter
Hemp protein is a complete protein, meaning it provides all nine essential amino acids in one convenient package. It's like ordering a pre-assembled toolkit for your body, instead of having to search for each tool individually. Many plant-based proteins are incomplete, lacking one or more essential amino acids. This means you'd have to carefully combine different plant sources to ensure you’re getting everything you need.
But with hemp protein, you get the full set. This isn't just about convenience, it's about maximizing your body's efficiency. When all essential amino acids are present simultaneously, your body can put them to work immediately, like a well-coordinated construction crew. This is particularly important for processes like muscle protein synthesis, essential for building and repairing muscle tissue.
Recognizing the Signs of Deficiency
Your body is pretty good at telling you when something’s off. While serious amino acid deficiencies are rare, suboptimal intake can still lead to noticeable symptoms. Think of it as your body’s foreman sending out warning signals.
Here are some signs to watch out for:
- Low energy levels: Amino acids are involved in energy production. Not enough, and you might feel constantly drained.
- Mood swings: Some amino acids are precursors to neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers in your brain that regulate mood. An imbalance can lead to mood instability.
- Impaired immune function: Amino acids are key players in building and maintaining a strong immune system.
- Muscle weakness or loss: Without sufficient amino acids, your body struggles to repair and build muscle tissue.
- Difficulty sleeping: Tryptophan, an essential amino acid, helps produce melatonin, the hormone that regulates your sleep-wake cycle.
Let's dive deeper into the essential and non-essential amino acids with this helpful table:
Essential vs Non-Essential Amino Acids: The Complete Guide
This table breaks down the key differences between essential amino acids (which you need to get from your diet) and non-essential amino acids (which your body can produce). Understanding these distinctions can help you make informed choices about your protein intake.
| Amino Acid | Type | Primary Benefits | Common Food Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Histidine | Essential | Growth and repair of tissues, production of red and white blood cells | Meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, soybeans |
| Isoleucine | Essential | Muscle metabolism, energy regulation, immune function | Meat, fish, poultry, eggs, dairy, nuts, seeds, legumes |
| Leucine | Essential | Muscle protein synthesis, wound healing, blood sugar control | Meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, soybeans, lentils |
| Lysine | Essential | Calcium absorption, energy production, collagen formation | Meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, soybeans, spirulina |
| Methionine | Essential | Tissue growth, metabolism, detoxification | Meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, Brazil nuts, sesame seeds |
| Phenylalanine | Essential | Production of neurotransmitters (dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine) | Meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, soybeans, nuts, seeds |
| Threonine | Essential | Collagen and elastin formation, immune function, fat metabolism | Meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, lentils, nuts |
| Tryptophan | Essential | Serotonin and melatonin production, mood regulation, sleep | Meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, soybeans, nuts, seeds |
| Valine | Essential | Muscle growth and repair, energy production | Meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, soybeans, lentils, peanuts |
| Alanine | Non-essential | Energy production, glucose metabolism | Meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, nuts, legumes |
| Arginine | Conditionally essential | Wound healing, immune function, hormone release | Meat, poultry, fish, dairy, nuts, seeds, legumes |
| Asparagine | Non-essential | Nervous system function, protein synthesis | Seafood, asparagus, dairy, potatoes, nuts, seeds, legumes |
| Aspartic acid | Non-essential | Nervous system function, fatigue reduction | Meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, nuts, seeds, legumes |
| Cysteine | Conditionally essential | Antioxidant, detoxification, protein structure | Meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, oats, garlic, onions |
| Glutamic acid | Non-essential | Learning and memory, neurotransmission | Meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, nuts, seeds, legumes |
| Glutamine | Conditionally essential | Intestinal health, immune function, muscle recovery | Meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, cabbage, beets, spinach |
| Glycine | Non-essential | Wound healing, collagen formation, muscle growth | Meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, soybeans, spinach, kale |
| Proline | Non-essential | Collagen production, joint health, skin health | Meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, cabbage, mushrooms, asparagus |
| Serine | Non-essential | Muscle growth, immune function, cognitive function | Meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, soybeans, wheat gluten |
| Tyrosine | Conditionally essential | Production of thyroid hormones, stress response | Meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, nuts, seeds, legumes |
By understanding the roles of essential amino acids and recognizing the signs of potential deficiency, you can make informed decisions about your diet. Incorporating complete protein sources like hemp can help you ensure you're getting enough of these vital nutrients to support your body’s needs.
Plant Protein Showdown: How Hemp Really Stacks Up
Think of choosing a plant-based protein like picking a smartphone. Each one has its own strengths and weaknesses. Hemp protein is no different. To understand where it fits, let’s compare it to some other popular plant-based options like pea protein, brown rice protein, soy protein, and quinoa protein. Each brings something unique to the table. Pea protein, for example, boasts high levels of lysine, while rice protein is known for being easy on the digestion. Soy protein is a "complete" protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids, but it's also a common allergen. Quinoa protein stands out with its unique mineral profile.
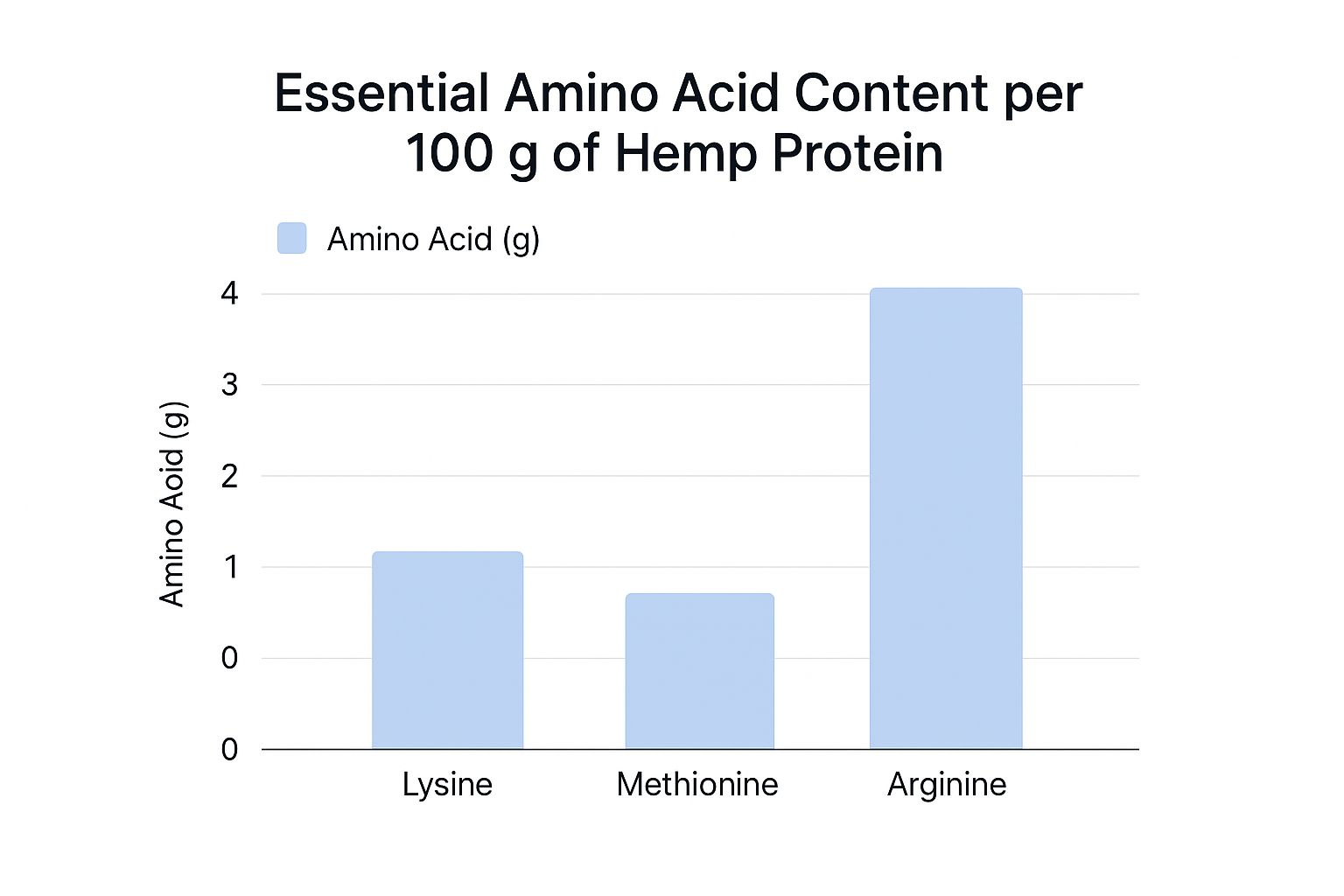
This infographic gives us a visual snapshot of hemp protein's essential amino acid content, specifically lysine, methionine, and arginine, per 100g. Notice the respectable amount of arginine, a conditionally essential amino acid. While hemp protein does contain lysine and methionine, these are often its limiting amino acids, meaning they are present in lower amounts compared to other proteins. Like many plant-based proteins, hemp also contains beneficial trace minerals that contribute to overall health.
Understanding Protein Quality

This screenshot highlights the important concept of protein quality. It's not just about which amino acids are present, but also how well your body can actually use them – in other words, their digestibility. Different protein sources are evaluated based on their ability to deliver the essential amino acids our bodies need. A complete amino acid profile doesn’t automatically mean your body will absorb and utilize it efficiently.
Interestingly, the amino acid composition and protein quality of hemp protein can vary depending on how it's processed and even the variety of hemp plant used. A 2023 study in 'Food Science & Nutrition' analyzed three different hemp protein sources and found amino acid scores (PDCAAS) ranging from 0.46 to 0.50 out of a possible 1.0. This tells us that hemp protein is less digestible than some high-quality animal proteins, but it’s still a valuable source of nutrition. You can dive deeper into the study's findings here.
Combining Plant Proteins for a Complete Profile
While hemp protein does offer a complete amino acid profile, the lower levels of some essential amino acids, like lysine, mean we can get even more out of it by strategically combining it with other plant proteins. Think of it like building a well-rounded team – each member contributes different skills.
Pairing hemp protein with pea protein, for instance, is a smart move. The pea protein’s abundance of lysine compensates for hemp’s lower levels, while still allowing you to benefit from hemp’s strengths. This creates a synergistic effect, delivering a more balanced and complete amino acid profile than either protein could offer alone. This is a particularly valuable strategy for vegans and vegetarians looking to optimize their protein intake.
The Digestibility Reality Check: What Actually Gets Absorbed
Having a great hemp protein amino acid profile is like having a top-notch toolbox. It’s full of potential, but useless if you don't know how to use the tools. Your body needs to effectively break down and absorb those amino acids. This is where digestibility comes in – it's the key to unlocking hemp protein's power.
Hemp protein has unique characteristics that affect how your digestive system processes it. Think of it like different types of gasoline: some cars need premium, while others run fine on regular. Our digestive systems are similar–understanding how hemp protein interacts with yours is crucial. For a deeper look, check out this article: The Bioavailability of Hemp Protein: Why It’s Better Than Other Plant Proteins.
Factors Affecting Hemp Protein Absorption
Several factors influence how well you absorb hemp protein. Processing methods, for example, are important. Some methods can damage amino acids, like leaving your tools out in the rain – they’re still there, but not as effective.
Individual digestive systems also vary. Some people process hemp protein easily, while others might have trouble. Factors like gut health, enzyme levels, and even hydration can impact absorption. It’s like having different soil conditions – some plants thrive, while others struggle.
This screenshot shows the Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS). This score measures protein quality based on amino acid content and digestibility. It tells you how well a protein provides the essential amino acids your body needs and how easily they're absorbed. A higher score means a more complete and digestible protein.
Optimizing Hemp Protein Digestion
Luckily, there are ways to improve hemp protein absorption. Timing is key. Consuming hemp protein around workouts, when your body is ready to rebuild muscle, can maximize its use. It’s like having supplies delivered right when the construction crew needs them.
Preparation methods can also boost bioavailability. Soaking or sprouting hemp seeds before eating them can improve nutrient absorption. Think of it like preparing ingredients before cooking – it brings out the best flavors and makes them easier to digest.
Combining hemp protein with other foods can further improve its benefits. Pairing it with enzyme-rich foods, like papaya or pineapple, can aid digestion. This is like using the right tools for the job – it makes the whole process more efficient. These simple strategies can help your body unlock the full nutritional power of hemp protein's complete amino acid profile.
Smart Hemp Protein Strategies That Actually Work
Knowing about hemp protein's benefits is great, but actually using that knowledge is even better. Think of it like having all the ingredients for a cake but never actually baking it! This section bridges the gap between the science of hemp protein’s amino acid profile and practical, everyday use. We’ll explore how to get the most out of this plant-based protein powerhouse, tackling real-world issues like taste, preparation, and how to fit it into a busy lifestyle.

This image shows how versatile the hemp plant truly is. Its uses go way beyond nutrition, extending to textiles and even building materials. Hemp’s sustainability makes it an incredibly valuable resource. It's a good reminder that the hemp protein in our smoothies and snacks comes from a plant with a wide range of amazing applications.
Addressing Lysine: The Limiting Amino Acid
Hemp protein boasts a complete amino acid profile, meaning it contains all the essential building blocks our bodies need. However, its lysine content is sometimes lower compared to other protein sources. Lysine is like a vital key that unlocks the full potential of protein synthesis. To make sure we’re getting enough, we can strategically combine hemp protein with other foods. Think of it like building a balanced meal—different foods work together to provide all the nutrients we require.
- Pairing with legumes: Combining hemp protein with lentils, beans, or chickpeas in a meal significantly increases your total lysine intake. This creates a powerful synergy, enhancing the overall quality of the protein you’re consuming.
- Boosting with grains: Certain grains like quinoa and amaranth are also good sources of lysine and complement hemp protein perfectly. This simple combination creates a complete and balanced protein source, ensuring you’re getting everything your body needs.
Preparation Methods That Preserve Nutrients
Just like overcooking vegetables can diminish their vitamin content, the way you prepare hemp protein affects how much of its amino acid goodness you actually absorb.
- Gentle blending: Adding hemp protein to smoothies or shakes is a fantastic way to avoid heat, which can damage delicate proteins. This keeps the amino acids intact and readily available for your body to use.
- Sprinkling on food: A simple sprinkle of hemp protein on salads, yogurt, or oatmeal adds a nutritional boost without altering its amino acid profile. It’s a quick and easy way to enhance the protein content of your meals.
- Baking at lower temperatures: If you’re baking with hemp protein, using lower temperatures and shorter cooking times helps preserve its nutritional value. For tips on preserving the quality of various foods, checking out resources on natural food preservation can be beneficial.
Timing and Portioning for Optimal Absorption
When and how much hemp protein you consume plays a role in how well your body absorbs and uses it.
- Post-workout boost: Consuming hemp protein after a workout helps repair muscle tissue and replenish those essential amino acid stores, aiding in recovery and growth.
- Spreading intake throughout the day: Instead of consuming one large serving, consider dividing your hemp protein intake throughout the day, incorporating it into multiple meals and snacks. This approach can lead to better absorption and provide a consistent supply of amino acids for your body to utilize.
- Portion control: Starting with smaller portions (around 1-2 tablespoons) and gradually increasing the amount as needed allows your body to adjust and helps prevent any digestive discomfort.
Making Hemp Protein Palatable
Let’s face it, the earthy flavor of hemp protein isn’t always a crowd-pleaser. But there are clever ways to make it more appealing without compromising its nutritional value.
- Masking the flavor: Adding fruits, spices, or natural sweeteners like vanilla, chocolate, or cinnamon to smoothies or shakes can effectively mask the earthy taste of hemp protein. Experiment with different flavor combinations to find your favorites!
- Incorporating into savory dishes: Hemp protein can also be blended seamlessly into soups, sauces, or dips, where the earthy flavor complements the overall taste profile rather than overpowering it.
By putting these practical strategies into action, you can unlock the full potential of hemp protein's impressive amino acid profile and make it a valuable and enjoyable part of a healthy eating plan.
Who Benefits Most From Hemp Protein's Complete Profile

This image showcases the wide array of plant proteins available, a testament to their increasing role in modern nutrition. Plant-based proteins are gaining traction, and understanding their unique strengths and weaknesses is key to making smart dietary choices. As we'll explore, hemp protein offers specific benefits that make it an attractive option for certain people.
Hemp protein, despite its complete amino acid profile, isn't a universal solution. Its distinctive qualities, however, make it especially advantageous for particular groups. For instance, those with sensitive stomachs often find hemp protein more agreeable than other protein sources. This is partly thanks to its fiber content, which supports healthy digestion. To manage cravings and use hemp protein effectively, consider strategies similar to those used to curb sugar cravings: Smart Hemp Protein Strategies That Actually Work.
Hemp Protein for Specific Needs
Let's delve into who can truly reap the rewards of adding hemp protein to their diet:
-
Aging Adults: Maintaining muscle mass becomes increasingly important as we age. Hemp protein's complete amino acid profile provides the essential building blocks for muscle protein synthesis, promoting healthy aging.
-
Digestive Sensitivities: Those with conditions like IBS often find certain protein sources problematic. Hemp protein’s gentle nature and fiber content can be easier on the digestive system. For more on hemp protein's advantages, see our article: Top Benefits of Hemp Protein for Better Health.
-
Endurance Athletes: Intense exercise can lead to increased inflammation. Hemp protein’s anti-inflammatory properties, coupled with its complete amino acid profile, can aid recovery and lessen muscle soreness.
-
Multiple Food Sensitivities: If you have allergies or intolerances to common protein sources like soy or dairy, hemp protein might be a welcome relief. It’s a complete protein source without the usual allergens.
Sustainability and Long-Term Use
Beyond its nutritional value, hemp protein is also a sustainable protein source. Hemp cultivation requires less water and fewer pesticides compared to many other crops, making it an environmentally conscious option. This sustainability aspect often resonates with those looking for a long-term protein source aligned with their values. Its relatively mild flavor also allows for easy integration into various recipes, encouraging regular consumption. These combined benefits make hemp protein a strong contender in the plant-based protein world.
Your Hemp Protein Decision Framework
After diving deep into the amino acid profile of hemp protein, let's figure out how to actually use that knowledge. This section will help you decide if hemp protein fits your personal nutritional needs. We'll tackle common questions, bust some myths, and set realistic expectations about what hemp protein can and can't do.
Evaluating Hemp Protein Products
Shopping for protein powders can be a bit like navigating a maze. Here's a checklist to help you assess hemp protein products:
-
Amino Acid Profile: Aim for a complete profile. Hemp naturally contains all nine essential amino acids, but sometimes processing can affect the amounts.
-
Sourcing and Processing: Choose organically sourced hemp protein that’s minimally processed. This helps keep the amino acids intact.
-
Added Ingredients: Check the label for unnecessary fillers, sweeteners, or artificial flavors. Keep it clean and simple!
-
Third-Party Testing: Seals of approval from third-party testing verify quality, purity, and accurate labeling. It’s an added layer of trust.
Integrating Hemp Protein Into Your Diet
Here are some things to think about when adding hemp protein to your diet:
-
Dietary Approach: Hemp protein is adaptable. It works well in vegan, vegetarian, and omnivorous diets.
-
Budget: Hemp protein offers good value, but compare the nutrition you get per dollar when comparing different products.
-
Taste Preferences: Hemp has an earthy flavor. You can easily blend it into smoothies or mix it into savory dishes to mask the taste.
When Hemp Protein Might Not Be Ideal
Hemp protein isn't a magic bullet. It might not be the right fit if:
-
Severe Lysine Deficiency: Hemp is a complete protein, but it’s lower in lysine. If you have a serious lysine deficiency, address that first.
-
Specific Allergies: Hemp allergies are uncommon, but they do exist. Be careful if you have allergies to plants in the Cannabis sativa family.
-
Seeking Maximum Muscle Hypertrophy: Hemp helps with muscle growth, but whey protein typically has more branched-chain amino acids, which are key for maximizing muscle gain.
Making Informed Choices
Think of this decision framework as your guide to the world of hemp protein. It’s all about understanding your needs and making choices based on real information, not marketing hype. Now, let’s see how Cantein offers solutions to many of the points we’ve discussed.
Ready to see what high-quality hemp protein can do for you? Visit Cantein to explore our organic hemp protein products and discover how they can help you reach your health and fitness goals.

