Understanding What Makes Protein Powder Actually Digestible
Imagine your digestive system is a sophisticated assembly line. Certain materials move through with ease, while others create bottlenecks and slowdowns. This is precisely why one person can down a protein shake and feel great, while another is left dealing with uncomfortable bloating and gas. The key to finding an easy to digest protein powder isn't a secret formula, but an understanding of what makes a protein "gut-friendly" to begin with. It's not about magic; it's about the specific, physical traits of the protein itself.
The journey from a scoop of powder to the amino acids your muscles can use depends on a few critical factors. These characteristics determine whether the protein cooperates with your body or works against it, directly shaping your digestive experience.
Protein Structure and Molecular Size
On a microscopic scale, proteins are long, complicated chains of amino acids twisted into intricate shapes. Picture one protein as a tightly wound ball of yarn and another as a single, straight piece of thread. Your digestive enzymes can snip the straight thread into usable pieces far more easily than they can unravel the complex, knotted ball.
This is where smart processing plays a huge role. Techniques like hydrolysis essentially "pre-digest" the protein. This process breaks down the complex structures into smaller, more accessible pieces called peptides. Because these molecules are smaller, they demand less effort from your stomach and intestines, which leads to quicker absorption and fewer digestive issues.
The Role of Processing and Purity
The way a protein is manufactured significantly impacts how well you can digest it. The aim of high-quality processing is to isolate the pure protein and get rid of other components that can cause digestive trouble, like fats, carbs, and especially lactose.
- Concentrates: This is the most basic form of protein powder. While they contain a solid amount of protein (typically 70-80%), they also have more fat and lactose, which can be a major trigger for people with sensitivities.
- Isolates: This version goes through extra filtering to strip out most of the fats and lactose. The outcome is a much purer protein (90% or higher) that is considerably gentler on the digestive system.
- Hydrolysates: As we touched on, these are the "pre-digested" proteins. They are broken down into the smallest possible fragments for the most rapid absorption available.
The market has clearly shifted to meet the growing demand for cleaner, more refined protein options. Whey protein isolate (WPI), for instance, has become a top choice in the easy to digest protein powder category because of its high purity. In fact, global sales of whey basic protein isolate are projected to climb past $11.53 billion by 2035, showing just how popular and effective it is for consumers who prioritize digestive comfort. You can learn more about these market trends and what they mean for shoppers in detailed industry reports.
Ultimately, picking the right powder isn't just about the source—it's about how that source was prepared. A highly filtered isolate or a hydrolyzed powder provides a smoother journey through your digestive tract, helping you reap the rewards of protein without the uncomfortable downsides. This intense focus on purity and molecular size is what truly distinguishes a standard powder from one designed for digestive ease.
Why Your Gut Health Determines Everything About Protein Success

Your digestive system does much more than just process food; it’s the control panel for your overall health. Think of it like the foundation of a house. If the foundation is weak, it doesn't matter how great the rest of the building materials are—the entire structure will be unstable. Similarly, if your gut health is off, even the most premium protein powder won't give you the benefits you're hoping for. This is precisely why finding an easy to digest protein powder is now a top goal for so many people.
When your gut isn't working properly, it can undermine your fitness goals. An imbalanced digestive system struggles to break down nutrients and absorb them effectively. This means a large chunk of the protein you consume could pass right through you without ever reaching your muscles, essentially becoming expensive waste. If you've ever felt bloated or uncomfortable after a protein shake, your body is likely signaling that there's a problem with the absorption process.
The Gut-Brain Connection and Protein
The relationship between our gut and our general well-being is powerful. An irritated gut, often bothered by proteins that are tough to break down, can send stress signals throughout your body. This communication superhighway is called the gut-brain axis, and it directly connects your digestive tract to your central nervous system. As a result, digestive issues can affect everything from your mood and energy to your immune system.
This is where a gentle, well-made protein powder can make a huge impact. An easy to digest protein powder works with your digestive system, not against it. By picking a formula created for easy absorption, you're not just feeding your muscles—you're supporting your gut health. This helps calm inflammation and promotes a healthy gut microbiome, letting your body get the most out of every single scoop.
Why Traditional Powders Often Fail
Many standard protein powders contain ingredients that can upset your gut, even if you don't have known sensitivities. Common offenders include:
- High Lactose Content: Often found in whey concentrates, lactose is a frequent cause of gas and bloating.
- Artificial Sweeteners and Fillers: Additives like sucralose or gums can irritate the gut lining and harm beneficial gut bacteria.
- Harsh Processing: Some manufacturing methods can leave proteins in a state that's difficult for your body to digest.
A growing understanding of these problems is changing how people shop for supplements. Consumers are now looking for cleaner products that work without causing digestive side effects. This shift is a key reason why the protein supplements market is projected to expand from $27.28 billion in 2024 to $52.34 billion by 2033. This growth highlights a clear demand for products that offer real results without the digestive distress. You can explore the full protein supplements market forecast to see how these preferences are reshaping the industry. Choosing a powder that supports your body is the secret to achieving real protein success.
Decoding The Best Protein Types For Sensitive Stomachs
Picking a protein powder can feel like choosing the right fuel for a car. If you put the wrong kind in, you’ll likely experience sputtering and poor performance. This is especially true if you have a sensitive stomach, making the choice of protein even more important. Let's break down the most common types to find out which are best for digestive comfort.
Whey Protein: The Isolate vs. Concentrate Difference
Whey protein is a very common choice, but it comes in a few different forms. Whey concentrate is the most basic version. While it’s great for building muscle, it contains higher amounts of lactose and fat, which often cause bloating and gas for people with sensitivities.
Whey protein isolate, on the other hand, is a more refined option. It goes through a filtering process that strips out most of the lactose and fat, leaving a product that is often over 90% pure protein. This purification makes it an excellent easy to digest protein powder for those who are sensitive to dairy but still want the muscle-building benefits of whey.
For the most sensitive individuals, hydrolyzed whey goes one step further. The protein is "pre-digested" with enzymes, breaking it into smaller pieces called peptides. This means your digestive system has less work to do, leading to very fast and easy absorption.
Plant-Based Proteins: A Gut-Friendly Revolution
Plant-based proteins have grown in popularity, and not just among vegans. They are naturally lactose-free and tend to be gentle on the gut. But just like with whey, not all plant proteins are the same.
- Pea Protein: Sourced from yellow split peas, this is a solid choice because it’s rich in branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) and is usually very easy to digest.
- Rice Protein: Typically made from brown rice, this protein is hypoallergenic and gentle, making it a safe option for almost anyone.
- Hemp Protein: Hemp is a standout because it’s a complete protein that also provides fiber and healthy fats, which can support good gut health. If you want to learn more, our complete guide on finding the best protein powder for a sensitive stomach offers a deeper look.
To help you decide, the table below compares the key features of major protein types, focusing on what matters most for digestive health.
Digestibility Comparison: Major Protein Types
Compare absorption rates, lactose content, and digestive ease across different protein powder types
| Protein Type | Absorption Speed | Lactose Content | Digestive Ease | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whey Concentrate | Moderate | High | Low | Budget-conscious users without dairy sensitivity. |
| Whey Isolate | Fast | Very Low / None | High | Dairy-sensitive individuals wanting fast absorption. |
| Hydrolyzed Whey | Very Fast | None | Very High | Maximum speed and minimal digestive stress. |
| Pea Protein | Moderate | None | High | Vegans or those needing a hypoallergenic option. |
| Rice Protein | Moderate | None | Very High | Extremely sensitive individuals; hypoallergenic. |
| Hemp Protein | Slower | None | High | Those wanting protein plus fiber and healthy fats. |
This comparison shows that if you want the benefits of whey without the discomfort, whey isolate is a great choice due to its low lactose content. However, plant-based options like pea and rice protein are excellent, gentle alternatives that are naturally free of common irritants.
The infographic below offers a visual comparison of whey isolate against two popular plant-based choices.
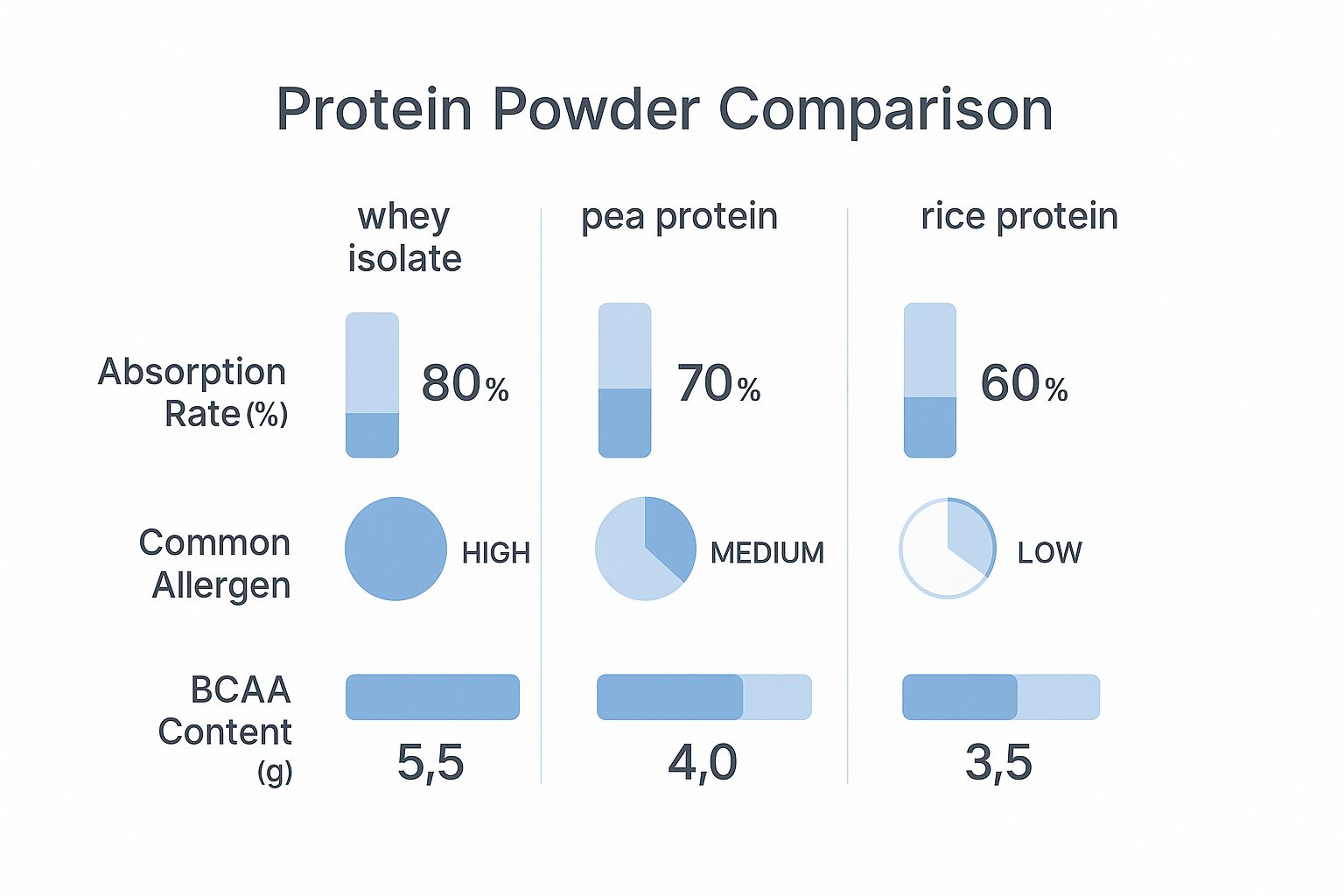
As you can see, while whey isolate absorbs quickly and is packed with BCAAs, plant-based proteins like pea and rice offer fantastic digestibility with a much lower chance of causing an allergic reaction. Ultimately, the best choice is about matching the protein's profile to your body's unique needs.
Reading Labels Like A Pro: Spotting Digestive Troublemakers
Choosing an easy to digest protein powder isn't just about the main protein source. Often, the real troublemakers causing bloating and gas are the other ingredients on the label—the sweeteners, thickeners, and fillers added for better taste and texture. Think of your protein as the star of the show; if the supporting cast is off, the entire performance can be ruined. To shop smart, you need to look beyond the protein grams and learn to read the entire ingredient list.
To give you an idea of what you might see, here is a nutritional panel from a standard protein powder.

This example shows that a product contains more than just protein. It has a mix of fats, carbs, and often a long list of additives. The trick is learning to tell the difference between helpful ingredients and the ones that might upset your stomach.
The Most Common Digestive Culprits
When you're scanning a label, a few categories of ingredients should be a red flag, especially if you have a sensitive gut. These are frequently added to protein powders but can interfere with smooth digestion.
- Artificial Sweeteners: Watch out for ingredients like sucralose, aspartame, and acesulfame potassium. While common, they can disrupt your gut bacteria and are a frequent cause of bloating and gas for many people.
- Sugar Alcohols: Erythritol, xylitol, and sorbitol are popular low-calorie sweeteners. Though often better than sugar, your body doesn't fully absorb them, which can lead to digestive issues when consumed in larger amounts.
- Thickeners and Gums: Ingredients like xanthan gum, guar gum, and carrageenan are used to give shakes a smoother, thicker consistency. However, they can also slow down digestion, leading to stomach discomfort or a heavy feeling.
- Fillers: Some brands add extra ingredients like maltodextrin (a processed carb) to increase the volume of the powder. These offer little nutritional benefit and can cause a spike in blood sugar, which isn't ideal for everyone.
Spotting the Gut-Friendly Additions
On the other hand, some ingredients are specifically included to improve digestion and make the protein powder gentler on your system. Seeing these on a label is a good sign that the product was formulated with your gut health in mind.
Keep an eye out for these helpful additions:
- Digestive Enzymes: A blend containing enzymes like protease (for protein), amylase (for carbs), and lipase (for fats) can seriously improve how well you absorb nutrients and reduces the stress on your gut.
- Probiotics: These are the "good" live bacteria that help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, which is crucial for proper digestion and overall wellness.
- Prebiotics: Ingredients like inulin or certain fibers act as food for your beneficial gut bacteria, helping them to flourish.
By learning to spot these "friend or foe" additives, you can look past the flashy claims on the front of the tub. This empowers you to make a smart decision based on the complete ingredient list, ensuring you pick an easy to digest protein powder that truly supports your body.
How Your Body Actually Processes Different Proteins
To pick a protein supplement that truly works for you, it helps to understand what happens after you take that first sip. Think of your digestive system as a highly specialized assembly line, and protein is the raw material. How efficiently your personal "factory" processes that material can make all the difference between feeling great and feeling bloated.
This is why finding an easy-to-digest protein powder is so crucial for avoiding discomfort. The entire digestive process depends on how well your body can break down large, complex protein molecules into their essential building blocks, called amino acids.
From Stomach Acid to Intestinal Absorption
Once you drink your protein shake, its first stop is the stomach. Here, strong stomach acid and a powerful enzyme named pepsin start to unwind the protein's tightly coiled structure. This initial step is a big deal. If a protein is particularly hard to break down, or if your stomach acid is on the weaker side, this stage can become a bottleneck, leaving you with that heavy, full feeling.
From the stomach, the partly digested protein moves into the small intestine. A team of specialized enzymes from the pancreas joins the effort, snipping the protein chains into even smaller pieces called peptides and, finally, into individual amino acids. These amino acids are then small enough to pass through the intestinal wall and enter your bloodstream, ready to be delivered to your muscles and tissues.
Why Your Individual Digestion Matters
How well your body handles this journey from shake to bloodstream depends on a few personal factors. Everyone's digestive system is unique.
Here's what can influence your experience:
- Digestive Enzyme Production: Some people naturally produce fewer of the specific enzymes needed to tackle protein. This can slow down the whole process and lead to digestive upset.
- Gut Bacteria Balance: Your gut is home to trillions of bacteria. A healthy and diverse microbiome helps with digestion, while an imbalance can lead to bloating and interfere with nutrient absorption.
- Protein Type and Timing: Fast-absorbing proteins like whey isolate are processed quickly, making them ideal after a workout. Slower-releasing proteins, like those found in certain plant sources, provide a more steady supply of amino acids. Our article on hemp protein for digestion explores how different plant options can offer unique digestive advantages.
To get a fuller picture, it's useful to understand how this fits into your overall metabolism. Learning more about how to measure metabolism can offer deeper insights into how your body uses nutrients.
Ultimately, your own biology determines which protein is right for you. One person might feel fantastic using whey, while another finds that a gentler, plant-based formula is the secret to getting results without the digestive downside. Recognizing these individual differences is the first step to building a protein strategy that truly supports your body.
Finding Your Perfect Digestible Protein Match
Now that you know what makes a protein powder gut-friendly, it’s time to find the one that’s right for you. This isn't about chasing a single "best" product, but rather matching a formula to your personal needs. Think of yourself as a detective for your own body—piecing together clues from your diet, fitness goals, and even your budget to identify the perfect easy to digest protein powder. This mindset will help you choose a supplement that supports your system instead of working against it.

A Step-By-Step Guide to Choosing Your Protein
To avoid digestive trouble and wasted money, a little planning goes a long way. Instead of just grabbing the most eye-catching tub on the shelf, start by looking at these key factors:
- Dietary Needs: This is your first and most important filter. If you're vegan or have a dairy intolerance, your search will automatically focus on plant-based options like pea, hemp, or brown rice protein. For those following a low-carb lifestyle, a protein isolate with minimal to no sugar is the clear winner.
- Fitness Goals: Why are you using protein powder? If your aim is to build muscle, look for a powder that delivers at least 20 grams of protein per serving and boasts a complete amino acid profile. If you're using it for weight management, a high-protein, low-calorie formula without added sugars can help you feel full and satisfied.
- Taste and Budget: Let’s be practical—if you can’t stand the taste or the price, you won’t stick with it. Many brands offer sample sizes, which are an excellent, low-risk way to try a new protein before you commit to buying a large container.
How to Test New Proteins Safely
Once you’ve found a promising candidate, ease it into your routine. Don't go from zero to a full scoop in one day. Start with a half-serving for a few days and listen to your body’s feedback. Subtle signs of poor tolerance can include mild bloating, a heavy feeling in your stomach, or a dip in your energy levels. If you notice any discomfort, it’s likely a sign that this particular formula isn’t a good match. This careful trial period helps you avoid major digestive issues and make a final choice based on how your gut actually feels.
To help you narrow down your options, the table below provides recommendations based on common digestive concerns.
| Digestive Concern | Recommended Protein Type | Key Features to Look For | Ingredients to Avoid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lactose Intolerance | Whey Protein Isolate, Plant-Based (Pea, Rice, Hemp) | "Lactose-free" or >90% protein purity, added lactase | Whey Protein Concentrate, Milk Solids, Casein |
| General Bloating/Gas | Plant-Based (Pea, Rice), Egg White Protein | Added digestive enzymes (protease, bromelain, papain) | Sugar Alcohols (sorbitol, mannitol), Inulin, Guar Gum |
| IBS or Sensitive Gut | Pea Protein Isolate, Brown Rice Protein, Collagen Peptides | Minimal ingredient list, certified low-FODMAP | Artificial Sweeteners (sucralose, aspartame), Thickeners |
| Gluten Sensitivity/Celiac | Any certified gluten-free protein (Whey, Plant, Egg) | "Certified Gluten-Free" seal | Wheat, Barley, Rye, Malt, cross-contamination warnings |
This selection guide can act as your starting point, helping you connect your specific needs to the right ingredients and formulas on the market.
The growing demand for better protein options has led to significant industry growth. The global protein powder market was valued at around USD 28.82 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 39.39 billion by 2029. This means more companies are creating specialized formulas for sensitive stomachs, giving you more choices than ever. You can discover more about protein powder market growth to see how these trends are shaping product availability. By using this systematic approach, you can confidently explore the market and find a protein that supports your health goals without causing digestive distress.
Maximizing Success: Pro Tips For Better Tolerance And Results
Choosing an easy to digest protein powder is a great first step, but how you use it can be the difference between feeling fantastic and dealing with discomfort. Even top-tier formulas can cause trouble if they aren't prepared and consumed with a little strategy. A few simple adjustments can significantly improve how well you tolerate your protein and boost your results, making sure you get every bit of value from each scoop.
The Art of Preparation and Timing
You might be surprised how much the way you mix and when you drink your shake can affect your digestion. Small changes here often lead to big improvements in how your body responds.
- Mix It Right: Shaking your protein powder in a shaker bottle is the go-to method, but if bloating is an issue, give a blender a try. The high-speed blending action breaks down the powder more completely, resulting in a smoother drink that's much gentler on your stomach.
- Watch the Temperature: For the best results, always mix your protein with cool or room-temperature liquids. Using hot water can cause certain proteins to denature, or clump up, which makes them far more difficult for your body to digest.
- Time It Smartly: If you find a shake on an empty stomach causes discomfort, try having it alongside a small meal or a snack with some healthy fats or fiber. This can help slow down digestion just enough for your system to process the protein without feeling overwhelmed.
Introducing New Proteins and Troubleshooting
When you bring a new protein into your routine, it's best to ease into it to prevent digestive shock. For the first few days, start with just a half-serving to see how your body reacts. If all feels well, you can move up to a full serving. This simple approach helps your system adapt smoothly.
If you're still running into problems, take a look at what you're mixing your protein with. The issue might not be the powder itself, but the milk, juice, or other ingredients in your smoothie. For a more detailed guide on optimizing your intake, our article on how to digest protein better provides even more tips and strategies.
Ultimately, finding success with protein supplements is all about building a routine that works in harmony with your body. By being mindful of preparation, timing, and how you introduce new formulas, you can minimize digestive stress and get the most out of your efforts.
Ready for a protein that’s designed for digestive success from the start? Discover Cantein’s organic hemp protein, a clean, simple formula created to fuel your body and support your gut health without the fillers or digestive troublemakers.

